Concept of Growth and Development
Growth and development refers to the physical, intellectual, social, emotional changes that occur in the person from womb to tomb.
Growth refers to physical changes that occur over time. These include changes in height, weight, fine motor and gross motor skills. These changes are more pronounced during childhood.
Development refers to physical changes as well as functional chganges (cognitive, social, emotional, moral, physical and behavioural).
These changes are studied and analyzed by different psychologist to understand how people grow and develop over period of time. Also, it is concerned of a different disciplines like psychology, anthropology, sociology, and neurological sciences.
Definition of growth:
According to Hurlock, “growth is a change in size in proportion, disappearance of old features and acquisition of new one.
Definitions of development:
According to E.B Hurlock, “ Development means a progressive series of changes that occur in orderly, predictable pattern as a result of maturation and experience.”
According to G.W. Allport, “ The developing individual cannot be thought of a thing in himself develop development in so far as it is considered to be produced from within, the individual himself alone is only a convenient of abstraction.”
According to liberty holders and Marmur development refers to a process of change in growth and capability over time as function of both maturation and interaction with the environment. Those development includes growth capability, maturation interaction with the environment.
Characteristics of development:
1. It is comprehensive in nature.
2. It is a continuous and integrated process.
3. It is quantitative as well as qualitative in nature.
4. Development is the product of both heredity and environment.
5. As development is also quantitative therefore, it is related to growth.
6. it is directional and multidimentional.
7. It is individualized and universal.
8. It is influenced by various factors such as biological, environmental and cultural.
9. It is shaped by both nature and nurture.
Characteristics of Growth:
1. It is quantitative in nature.
2. It is an intrinsic process.
3. It involves both the changes intrinsic as well as extrinsic.
4. It is measurable.
5. It is observable.
Principles of Growth and Development
The principles of growth and development help us to understand the various processes that occur in human as he progresses from infancy to adulthood. Human development is based on following principles:
1. Principle of directional development
Every human follows a certain pattern of development. Two important patterns of development are:
Cephalocaudal development: The word cephalic means head and the word caudal means tail. Thus, according to cephalocaudal principle, development proceeds from head to toe. In other words, upper body parts (head, brain, and sensory organs) develops first before the lower body parts.
Proximodistal development: The word proximal means center and the word distal means outward. Thus, according to Proximodistal principle, develpment proceeds from central part of the body to outwards. In other words, central part of the body (heart, lungs, and spinal cord) develops first before the peripheral part.
2. Principle of plasticity
Human development is characterized by plasticity i.e.; development is modifiable. Under the influence of the environment, an individual can improve or develop some skills. One example of human plasticity is the ability to learn a new language.
3. Principle of continuous development
Development is a continuous process that involves changes in all areas of life. From birth, a child goes through various stages of development such as infancy stage, early childhood stage, later childhood stage, adolescence stage, and adulthood stage. While going through these stages of development, a child continue to grow, learn, and change till his death.
4. Principle of predictability
Development is predictable. It can be predicted on the basis of biological and environmental factors. For example, children learn to crawl, sit up and walk at roughly the same ages. However, there can be some variation due to individual differences.
Other example, most children begin cooing between 3 and 5 months of age. They start babbling between 6 and 8 months of age. They start saying 1-2 words at 9 to 18 months.
5. Principle of interaction
• As the rate of development depends on genetic and environmental factors, therefore, development is a product of the interaction between heredity (nature) and environment (nurture).
• Also, development is a product of the interaction between maturation and learning. Both maturation and learning are interrelated to each other. For example, a child’s brain must reach a certain level of maturation before they can learn to walk and talk.
6. Principle of interrelation
Growth and developments are interrelated. Growth and development in one area of life affect the growth and development in other areas of life. Both growth and development depend on factors such as social, cognitive, physical, and emotional.
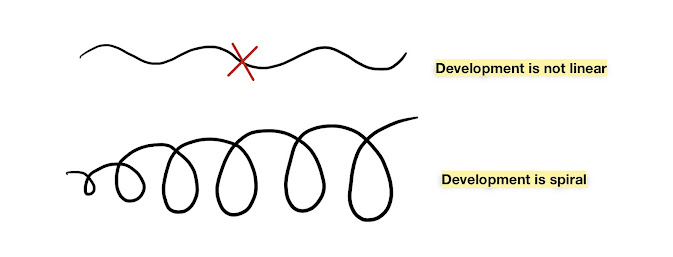
7. Principle of spiral development
Development is spiral and not linear because it does not takes place at a constant speed. During the infancy period of a child, the rate of growth and development is fast and then it slows down. But it again starts to increase during the adolescence period.
8. Principle of cumulative and recapitulatory development
Development is cumulative means adding new skills to previously learned skills. As the child gains experience, his skills keep improving.
Recapitulatory development means traits of one stage can be seen in other stages. For example, an introverted child is likely to remain introverted as he grows older.
9. Principle of differentiality
Development follows the principle of differentiality. Growth and development is continuous but not uniform. As we know, no two individuals are alike, therefore their rate of growth and development vary. For example,
• Girls grow faster than boys at the age of 12.
• some individuals mature earlier than others.
• The boys excel over girls in motor activities.
• During adolescence, physiological changes occur rapidly.
10. Principle of generality to specificity
Development proceeds from general to specific. It means children first develop basic skills and then proceed to the advanced ones. For example, children develop gross motor skills such as crawling, walking, and running before they develop motor skills such as writing and drawing.
11. Principle of simplicity to complexity
Development proceeds from simple to complex as children gain new experiences and skills. For example, children first learn to grab objects and then try to manipulate them in more complex ways. Other example, Children first learn basic arithmetic and numeral skills and then later use these skills to solve complex problems.
12. Principle of autonomy
Human development is autonomous. This principle of autonomy is more pronounced in early years of children. Autonomy helps children to become independent and make decisions based on their own reasoning.
Read also:
• Language development and Stages of language development
Frequently Asked Questions:
• What are 7 principles of human development ?
7 principles of human development are: Principle of directional development, principle of orderly development, principle of predictability, principle of cumulative development, principle of spiral advancement, principle of interaction, and principle of continuous development.
• What are 7 stages of human development?
7 stages of human development are: Pre-natal stage, infancy, early childhood, later childhood, Adolescence, early adulthood, and later adulthood.














0 Comments